- java.lang.Object
-
- org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.components.BeanEditForm
-
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- ClientElement, FormValidationControl
@SupportsInformalParameters @Events(value="prepare") public class BeanEditForm extends Object implements ClientElement, FormValidationControl
A component that creates an entire form editing the properties of a particular bean. Inspired by Trails and BeanForm (both for Tapestry 4). Generates a simple UI for editing the properties of a JavaBean, with the flavor of UI for each property (text field, checkbox, drop down list) determined from the property type (or by other means, such as an annotation), and the order and validation for the properties determined from annotations on the property's getter and setter methods. You may add block parameters to the component; when the name matches (case insensitive) the name of a property, then the corresponding Block is renderered, rather than any of the built in property editor blocks. This allows you to override specific properties with your own customized UI, for cases where the default UI is insufficient, or no built-in editor type is appropriate. BeanEditForm contains aFormcomponent and will trigger all the events of a Form.- See Also:
BeanModel,BeanModelSource,PropertyEditor,DataType,Form,Errors,BeanEditor
Component Parameters Name Type Flags Default Default Prefix add String literal A comma-separated list of property names to be added to the org.apache.tapestry5.beaneditor.BeanModel (only used when a default model is created automatically). autofocus boolean prop If true (the default), then the JavaScript will be added to position the cursor into the form. The field to receive focus is the first rendered field that is in error, or required, or present (in that order of priority). cancel boolean Since 5.2.0 prop If set to true, then the form will include an additional button after the submit button labeled "Cancel". The cancel button will submit the form, bypassing client-side validation. The BeanEditForm will fire a org.apache.tapestry5.EventConstants#CANCELED event (before the form's org.apache.tapestry5.EventConstants#VALIDATE event). class String message: private-core-components. beaneditform. class literal Specifies the CSS class attribute for the form; the factory default is "well". clientValidation org. apache. tapestry5. corelib. ClientValidation Not Null literal Controls when client validation occurs on the client, if at all. Defaults to org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.ClientValidation#SUBMIT. org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.ClientValidation#BLUR was the default, prior to Tapestry 5.4, but is no longer supported. exclude String literal A comma-separated list of property names to be removed from the org.apache.tapestry5.beaneditor.BeanModel (only used when a default model is created automatically). The names are case-insensitive. include String literal A comma-separated list of property names to be retained from the org.apache.tapestry5.beaneditor.BeanModel (only used when a default model is created automatically). Only these properties will be retained, and the properties will also be reordered. The names are case-insensitive. model org. apache. tapestry5. beaneditor. BeanModel prop The model that identifies the parameters to be edited, their order, and every other aspect. If not specified, a default bean model will be created from the type of the object bound to the object parameter. The add, include, exclude and reorder parameters are only applied to a default model, not an explicitly provided one. object Object Required prop The object to be edited. This will be read when the component renders and updated when the form for the component is submitted. Typically, the container will listen for a "prepare" event, in order to ensure that a non-null value is ready to be read or updated. Often, the BeanEditForm can create the object as needed (assuming a public, no arguments constructor). The object property defaults to a property with the same name as the component id. reorder String literal A comma-separated list of property names indicating the order in which the properties should be presented. The names are case insensitive. Any properties not indicated in the list will be appended to the end of the display orde. Only used when a default model is created automatically. submitLabel String message: core-submit-label literal The text label for the submit button of the form, by default "Create/Update". zone String literal Binding the zone parameter will cause the form submission to be handled as an Ajax request that updates the indicated zone. Often a Form will update the same zone that contains it. Component Events Name Description prepare Related Components
Simple Example
Using the bean editor, we can easily create a simple form for collecting information from the user. In this example, we'll collect a little bit of data about a User:
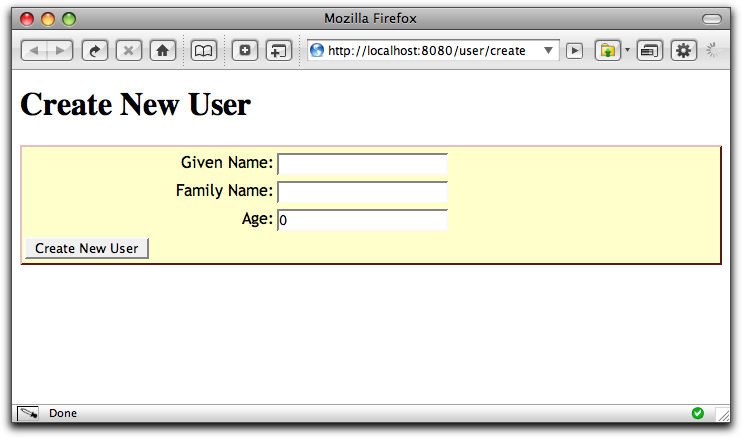
The bean to edit will be a property of the containing page.
User.java
import org.apache.tapestry5.beaneditor.NonVisual; public class User { private long id; private String firstName; private String lastName; private int age; public long getId() { return id; } @NonVisual public void setId(long id) { this.id = id; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }The @NonVisual annotation prevents the id from being displayed.
CreateUser.tml
<html xmlns:t="http://tapestry.apache.org/schema/tapestry_5_0_0.xsd" xmlns:p="tapestry:parameter"> <body> <h1>Create New User</h1> <t:beaneditform t:id="user" submitlabel="message:create-user"/> </body> </html>Nominally, we should have to bind the object parameter of the BeanEditForm component. However, as a convenience, Tapestry has defaulted the object parameter based on the component id. This works because the CreateUser class includes a property named "user", which matches the BeanEditForm component's id.
When the object to be edited is not a direct property of the page, it will be necessary to bind the object parameter explicitly. For example,
object="registration.address"to create or edit the address property of the page's registration property. Component ids may not contain periods, so there's no way to specify this without the object parameter. A best practice is to still explicitly set the component's id, thus:<t:beaneditform t:id="address" object="registration.address"/>CreateUser.properties
create-user=Create New User firstname-label=Given Name lastname-label=Family Name
We are using the page's message catalog to supply a messages. Externalizing such messages make them easier to work with, especially for an application that may be localized.
The
create-userkey is explicitly referenced (submitlabel="message:create-user"). This becomes the label on the submit button for the generated form.The two label keys will be picked up and used as the labels for the corresponding properties (in both the rendered
In many cases, common entries can be moved up to an application-wide message catalog. In that case, the page's own message catalog becomes a local override.
CreateUser.java
import org.apache.tapestry5.annotations.Persist; import org.apache.tapestry5.ioc.annotations.Inject; public class CreateUser { @Persist private User user; @Inject private UserDAO userDAO; public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } Object onSuccess() { userDAO.add(user); return UserAdmin.class; } }Notice that we don't instantiate the User object ourselves; instead we let the BeanEditForm component do that for us. It's capable of doing so because the User class has a default public no arguments constructor.
The onSuccess() method is invoked when the form is submitted with no validation errors (although client validation is enabled by default, server-side validation is always enforced). The UserDAO service is used to add the new user.
Returning a class from an event handler method (
UserAdmin.class) will activate the indicated page as the response page. As always, a redirect to to the response page is sent to the client.Validations and Overrides
By placing some annotations on the properties of the User class, we can enable client-side validations. In addition, we can override the default editor components for a property to add some additional instructions.
User.java (partial)
@Validate("required") public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } @Validate("required") public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } @Validate("min=18,max=99") public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }The new @Validate annotations added to the first name and last name properties indicates that a non-blank value must be provided. For the age property we are setting minimum and maximum values as well.
Validation for each field occurs when the form is submitted, and when the user tabs out of a field. If you submit immediately, Tapestry will display popup bubbles for each field identifying the error:
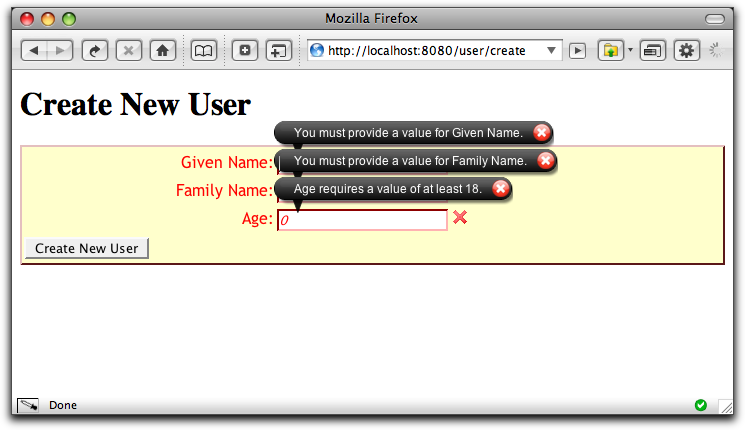
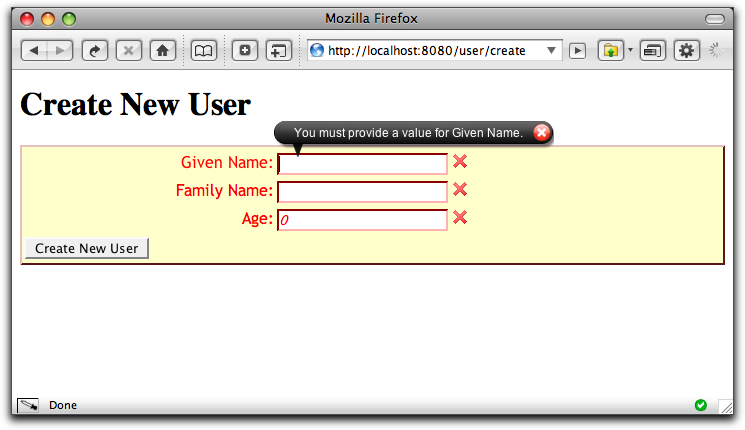
In addition, fields with errors are marked with a red X, the font for the first turns red, and the label for the field turns red. We're providing a lot of feedback to the user. After a moment, all the bubbles except for the current field fade. Bubbles fade in and out as you tab from field to field.
CreateUser.tml (partial)
We can customize how individual properties are editted. Here we'll add a small reminder next to the age property:
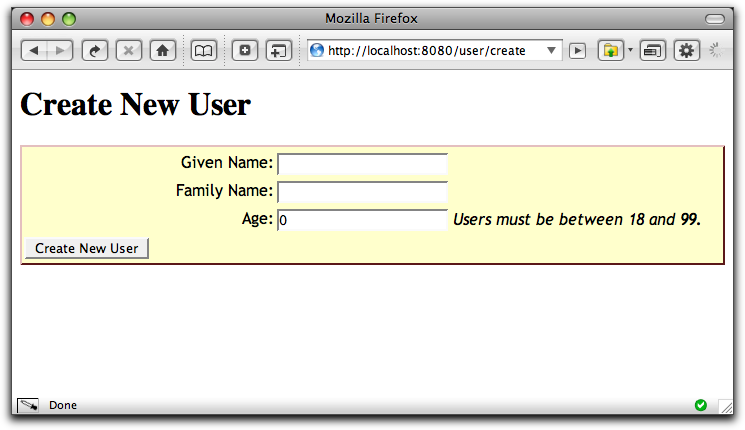
<t:beaneditform t:id="user" submitlabel="message:create-user"> <p:age> <t:label for="age"/> <t:textfield t:id="age" value="user.age"/> <em> Users must be between 18 and 99. </em> </p:age> </t:beaneditform>The
<p:age>element is an override for the property. The name is matched against a property of the bean. We need to provide a Label component, and an appropriate editor component.Notes
You can re-order the properties using the reorder parameter:
<t:beaneditform t:id="user" reorder="lastname,firstname"/>
You can accomplish the same thing by changing the order of the getter methods in the bean class. The default order for properties is not alphabetical, it is the order of the getter methods.
You can also remove properties with the exclude parameter, which is equivalent to the @NonVisual annotation.
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description BeanEditForm()
-
Method Summary
Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description voidclearErrors()InvokesValidationTracker.clear().StringgetClientId()Returns the client id of the embedded form.booleangetHasErrors()Returns true if the form'sValidationTrackercontains anyerrors.booleanisValid()Returns true if the form'sValidationTrackerdoes not contain anyerrors.voidrecordError(Field field, String errorMessage)A convenience method for invokingValidationTracker.recordError(Field, String).voidrecordError(String errorMessage)A convenience method for invokingValidationTracker.recordError(String).
-
-
-
Constructor Detail
-
BeanEditForm
public BeanEditForm()
-
-
Method Detail
-
getClientId
public String getClientId()
Returns the client id of the embedded form.- Specified by:
getClientIdin interfaceClientElement
-
clearErrors
public void clearErrors()
Description copied from interface:FormValidationControlInvokesValidationTracker.clear().- Specified by:
clearErrorsin interfaceFormValidationControl
-
getHasErrors
public boolean getHasErrors()
Description copied from interface:FormValidationControlReturns true if the form'sValidationTrackercontains anyerrors.- Specified by:
getHasErrorsin interfaceFormValidationControl
-
isValid
public boolean isValid()
Description copied from interface:FormValidationControlReturns true if the form'sValidationTrackerdoes not contain anyerrors.- Specified by:
isValidin interfaceFormValidationControl
-
recordError
public void recordError(Field field, String errorMessage)
Description copied from interface:FormValidationControlA convenience method for invokingValidationTracker.recordError(Field, String).- Specified by:
recordErrorin interfaceFormValidationControl
-
recordError
public void recordError(String errorMessage)
Description copied from interface:FormValidationControlA convenience method for invokingValidationTracker.recordError(String).- Specified by:
recordErrorin interfaceFormValidationControl
-
-