- java.lang.Object
-
- org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.base.AbstractField
-
- org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.base.AbstractTextField
-
- org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.components.TextField
-
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- ClientElement, Field
public class TextField extends AbstractTextField
TextField component corresponds to<input>element. The value parameter will be edited (read when the containingFormis rendered, and updated when the form is submitted). TextField is generally used with string values, but other values are acceptable, as long as they can be freely converted back and forth to strings. Includes thesizeattribute, if aWidthannotation is present on the property bound to the value parameter.Component Parameters Name Type Flags Default Default Prefix annotationProvider org. apache. tapestry5. ioc. AnnotationProvider prop Provider of annotations used for some defaults. Annotation are usually provided in terms of the value parameter (i.e., from the getter and/or setter bound to the value parameter). clientId String literal Used to explicitly set the client-side id of the element for this component. Normally this is not bound (or null) and org.apache.tapestry5.services.javascript.JavaScriptSupport#allocateClientId(org.apache.tapestry5.ComponentResources) is used to generate a unique client-id based on the component's id. In some cases, when creating client-side behaviors, it is useful to explicitly set a unique id for an element using this parameter. Certain values, such as "submit", "method", "reset", etc., will cause client-side conflicts and are not allowed; using such will cause a runtime exception. ensureClientIdUnique boolean Since 5.4 prop A rarely used option that indicates that the actual client id should start with the clientId parameter (if non-null) but should still pass that Id through org.apache.tapestry5.services.javascript.JavaScriptSupport#allocateClientId(String) to generate the final id. An example of this are the components used inside a org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.components.BeanEditor which will specify a clientId (based on the property name) but still require that it be unique. Defaults to false. nulls org. apache. tapestry5. NullFieldStrategy default nullfieldstrategy Defines how nulls on the server side, or sent from the client side, are treated. The selected strategy may replace the nulls with some other value. The default strategy leaves nulls alone. Another built-in strategy, zero, replaces nulls with the value 0. translate org. apache. tapestry5. FieldTranslator Required, Not Null translate The object which will perform translation between server-side and client-side representations. If not specified, a value will usually be generated based on the type of the value parameter. type String Not Null text literal Sets the type attribute of the <input>element. The default is "text", but this can be overridden when using <a href="http://www.w3.org/TR/html5/the-input-element.html">HTML5 types such as "number".validate org. apache. tapestry5. FieldValidator Not Null validate The object that will perform input validation (which occurs after translation). The validate binding prefix is generally used to provide this object in a declarative fashion. value Object Required prop The value to be read and updated. This is not necessarily a string, a translator may be provided to convert between client side and server side representations. If not bound, a default binding is made to a property of the container matching the component's id. If no such property exists, then you will see a runtime exception due to the unbound value parameter. Component Events Name Description parseClient toClient validate Related Components
Examples
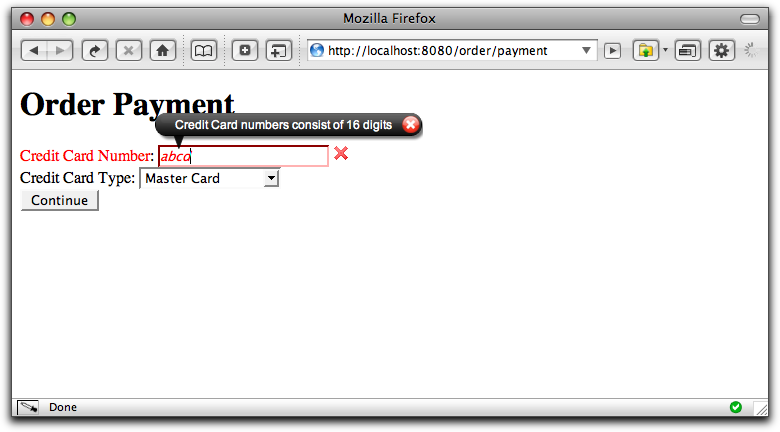
Once again, we're basing the example on the order payment screen from the Radio examples. This time we're focusing in on the text field used for entering the credit card number, and we're going to validate that number using a regular expression:
Payment.tml (partial)
<t:label for="cardNumber"/>: <t:textfield t:id="cardNumber" validate="required,regexp" size="20"/>The validate parameter is used to specify validations for the field. When it is omitted, the @Validate annotation of the property is used (if present). In any case, this references two of the built-in validations: "required" and "regexp".
This example presumes that the Payment page includes a property named "cardNumber".
The "required" validation requires no extra configuration. On the other hand, "regexp" needs to know the regular expression to enforce ... and it should also have a user presentable message.
Payment.properties (partial)
cardnumber-regexp-message=Credit Card numbers consist of 16 digits cardnumber-regexp=\\d{4}(\\-?\\d{4}){3}Tapestry uses the page's message catalog as a source of extra validation information. The key is the component id, the name of the validation. The value is given to the validator object ... here it's the regular expression for a credit card number (four sets of four digits, optionally seperated by dashes). The "-message" entry allows the normal error message for the validator to be overridden.
Notes
These same approaches apply consistently to all form control element components.
-
-
Field Summary
-
Fields inherited from class org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.base.AbstractField
cssClass, decorator, defaultProvider, disabled, environment, fieldValidationSupport, formSupport, javaScriptSupport, label, request, resources, validationTracker
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description TextField()
-
Method Summary
All Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description protected voidwriteFieldTag(MarkupWriter writer, String value)Invoked fromAbstractTextField.begin(MarkupWriter)to write out the element and attributes (typically, <input>).-
Methods inherited from class org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.base.AbstractTextField
getWidth, ignoreBlankInput, isRequired, processSubmission
-
Methods inherited from class org.apache.tapestry5.corelib.base.AbstractField
decorateInsideField, getClientId, getControlName, getLabel, isDisabled, putPropertyNameIntoBeanValidationContext, removePropertyNameFromBeanValidationContext, setDecorator, setFormSupport
-
-
-
-
Constructor Detail
-
TextField
public TextField()
-
-
Method Detail
-
writeFieldTag
protected void writeFieldTag(MarkupWriter writer, String value)
Description copied from class:AbstractTextFieldInvoked fromAbstractTextField.begin(MarkupWriter)to write out the element and attributes (typically, <input>). The controlName and clientId properties will already have been set or updated. Generally, the subclass will invokeMarkupWriter.element(String, Object[]), and will be responsible for including anAfterRenderphase method to invokeMarkupWriter.end().- Specified by:
writeFieldTagin classAbstractTextField- Parameters:
writer- markup write to send output tovalue- the value (either obtained and translated from the value parameter, or obtained from the tracker)
-
-